Everyting You Need to Know About Agile Crystal
Active or scrum?
Information technology's one of those project management questions that gets asked all the time. Is one better than the other? Which is correct for your projection or team?
Agile and scrum are very much related — cut from the same cloth, if yous will. But you need to empathise the major differences between them to answer the "which is correct for you" question.
What is agile?
The agile methodology came about in response to the rigidity of the traditional waterfall approach. With waterfall, phases are linear. The adjacent phase starts merely later the previous ane is complete.
Once a phase is done, going dorsum to brand changes is time-consuming, risky, and costly — hence, the demand for an agile culling that tin can keep up with changing demands and expectations.
With active project direction, piece of work happens in brusque, rapid cycles, and each wheel results in product releases that build on the previous product. Information technology's a project direction methodology that demands high levels of collaboration among a projection's stakeholders.
Agile espouses the continuous comeback mindset, which is why active ceremonies or meetings are a critical part of the process.
It allows organizations to continuously deliver products that friction match customer expectations, helping them thrive in an environs that's rife with volatility, doubt, and complication.
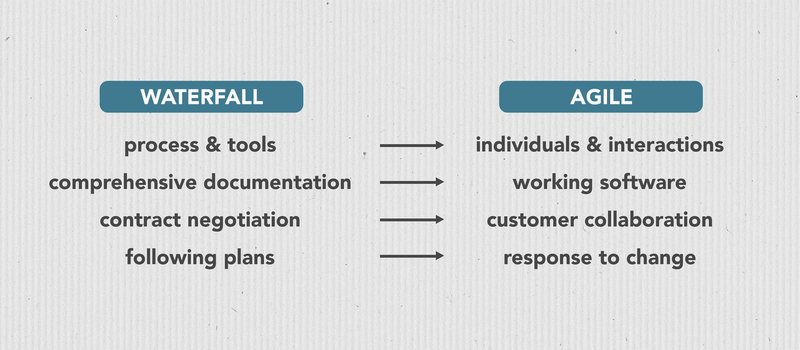
The Active Manifesto's four cadre values: (1) individuals and interactions over process and tools, (ii) working software over comprehensive documentation, (iii) customer collaboration over contract negotiation, and (4) response to change over following rigid plans.
Active's core values are divided into 12 principles.
- Provide customer satisfaction through early and continuous delivery of valuable software
- Accommodate irresolute requirements throughout the development process
- Oft deliver working software
- Maintain daily collaboration between developers and business stakeholders
- Motivate, trust, and support the individuals involved
- Use face-to-face conversations to convey information to the development squad
- Primarily mensurate progress through working software
- Back up sustainable development by establishing a maintainable and repeatable pace
- Pay continuous attention to good blueprint and technical excellence to raise agility
- Keep things simple by focusing on delivering the right value
- Self-organizing teams get stuff done
- Conduct regular reviews on how to become more effective and make adjustments accordingly
Advantages of the agile methodology
The agile procedure is popular for many reasons, specially in the Information technology and software development fields:
- Just the right corporeality of documentation: The traditional waterfall method requires long-term project planning and comprehensive documentation of each process step. In contrast, agile requires "just right" documentation to showtime a project, which can come up in the class of notes on a flipchart or whiteboard. Agile practitioners sometimes create descriptive documentation merely only if it brings value to the customer.
- Faster time to marketplace: One primary goal of active is to deliver a working product every bit soon equally possible, which can then be rolled out to actual users and enhanced based on their feedback.
- Accent on customer collaboration: The Agile Manifesto, which identifies the 4 central values and 12 principles that it thinks active practitioners must be guided by, underscores the importance of customer collaboration over contract negotiation. With active, teams and customers work together to achieve a common goal: a product that customers and end users actually want to use.
- Adapt to irresolute requirements: In agile, projects are broken down into phases or development cycles called iterations. Mail-iteration reviews and customer feedback dictate the next steps of the project, including the features to add together or remove.
Disadvantages of the agile methodology
Agile may be popular, but it's non perfect. As with all good things, it comes with a bad side, too.
- Difficult to assess how much effort is required: It'due south typical for active projects to commencement with but an idea of what the end product will await similar. This dubiousness makes it challenging to estimate how much work is required, particularly at the beginning of the project'south life cycle.
- Easy for the projection to go off rail: A detailed programme is not necessary to kick off an active project, and in many cases, in that location's not much to go on. If communication breaks down at any indicate during the project or feedback from customers is unclear, teams may concentrate on the wrong evolution areas, leading to telescopic pitter-patter, the project going over budget, and the terminal deliverable deviating from what was originally planned.
What is scrum?
Scrum is a framework that falls under the active umbrella. Similar to frameworks that follow agile principles, it banks heavily on team collaboration to evangelize high-value products. Work is done in sprints or time-boxed periods in which teams perform a specific amount of work.
Scrum squad
Every scrum team is equanimous of the following roles:
- Product owner: A key stakeholder responsible for the production'southward success. The product owner builds, manages, and prioritizes the product backlog (see "scrum artifacts" section below) and works closely with the development team to achieve the projection's desired result.
- Scrum primary: Responsible for championing scrum within the team. The scrum primary functions equally the glue that holds anybody together (i.e., concern, production owner, development team, and relevant individual roles).
- Development team: A self-organizing squad that typically includes developers, designers, testers, UX specialists, and operations engineers. They're responsible for doing the work and delivering a shippable production at the terminate of a sprint.
Scrum artifacts
According to Merriam-Webster, an artifact is "a usually simple object (such equally a tool or decoration) showing homo workmanship or modification as distinguished from a natural object." In other words, annihilation made by a human. The scrum process results in three primary artifacts, which indicate members' shared agreement of what needs to be done:
- Production backlog: Contains all the features, changes, fixes, and activities a team must achieve to achieve an upshot.
- Sprint excess: A list of all the product excess items that the team chooses to consummate inside a dart.
- Product increase: The sum of all the production backlog items completed in this and the previous sprints. It's what's produced at the conclusion of a sprint.
Scrum ceremonies
Scrum ceremonies are the events that happen inside a sprint. At that place are four of them, namely:
- Sprint planning: Done before a sprint begins. Teams define the scope of the sprint, set goals, hash out concerns, and constitute the details.
- Daily scrum: The daily standup normally lasts 15-30 minutes. Designed to become everyone on the same folio, points of discussion include what has been done, what's beingness done, what's next, and the issues impeding work progress.
- Sprint review: Takes place post sprint. Teams talk over which excess tasks have been completed and listen to user feedback to further improve the product.
- Sprint retrospective: Also takes place post sprint. Members reflect on the recently concluded dart to find out what went well and what didn't. Learnings are then applied to better time to come sprints.
Advantages of scrum
In that location'due south a reason why scrum is the most popular agile methodology.
- Availability of a working production while the project is ongoing: Scrum's delivery arrangement is incremental in nature — meaning, a product good plenty for the circumstances is released fifty-fifty while the project is underway, reducing time to market and increasing acquirement potential.
- High-quality product: Constantly checking in with end users and customers lets you know right away if the production is meeting their needs. If it doesn't, you can quickly change direction and deliver a much meliorate product inside only a few weeks.
- Improved user satisfaction: In the scrum approach, bodily user feedback plays a role in the evolution of the product, resulting in a high-quality deliverable that brings value to the client.
Disadvantages of scrum
Some scrum disadvantages yous need to be enlightened of include:
- No articulate definition, making the project difficult to plan: Without a articulate goal to aim for, particularly in the offset, the scrum master may have a difficult time organizing the project.
- A high degree of delivery from all stakeholders. For the scrum methodology to succeed, stakeholders must fully commit to collaboration and constant advice. They must nourish scrum events and report any updates or challenges. Otherwise, problems may arise.
Active vs. scrum: What'south the difference?
To further clarify the divergence between agile and scrum, consider the following:
- Agile is a full general approach to project management, whereas scrum is only 1 of the dissimilar ways to practice agile.
- Agile is a set of guiding principles and ideals, just it doesn't say how exactly those values should be implemented. Scrum is a framework that provides specific rules for getting things washed. For case, agile principle #12 is well-nigh reviews at regular intervals for performance improvement. In scrum, that is achieved through the sprint retrospective.
Bottom line, you can't actually choose between agile and scrum considering scrum is, in itself, agile. In other words, when y'all choose scrum to create software, yous're automatically also choosing to adhere to agile principles.
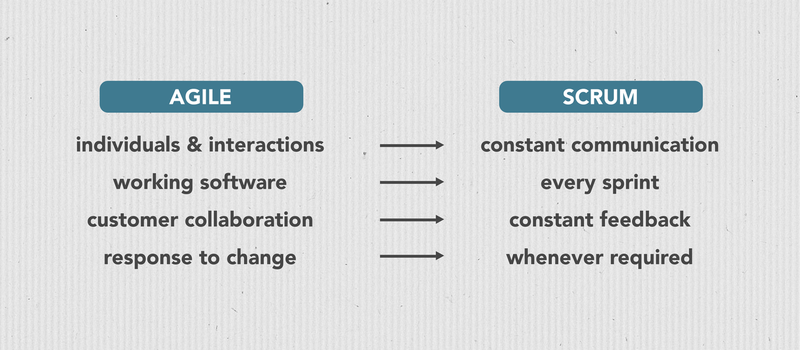
How scrum puts into practice the cadre agile values.
When to apply agile
When'due south the all-time time to use agile?
- If your team is flexible and can handle constant scope changes: Everyone has to be on board if active is to piece of work in your favor — from upper management to every member of your team.
- When yous need a working product released right away: If y'all need a shippable product released ASAP, y'all probably don't have much time to create a comprehensive plan.
- If changes volition have to be constantly implemented: When the product requires continuous refinement to accommodate to customer or manufacture needs, use agile.
When to use scrum
If you lot choose active over traditional methodologies, such as in the above scenarios, scrum is an selection to go for. To reiterate, if y'all choose scrum to develop a product, y'all've already chosen to go agile. Since at that place are other active frameworks besides scrum, the better question to ask is when should you use scrum over methods like kanban or farthermost programming (XP)?
Allow'south take a look.
Scrum vs. kanban
Kanban project management is a visual workflow management technique that uses kanban boards to dissever tasks, identify priorities, and motion tasks along several workflow stages until they're complete. Handy active tools y'all tin can use include project management software with built-in kanban boards such as Trello, Asana, and mon.com.
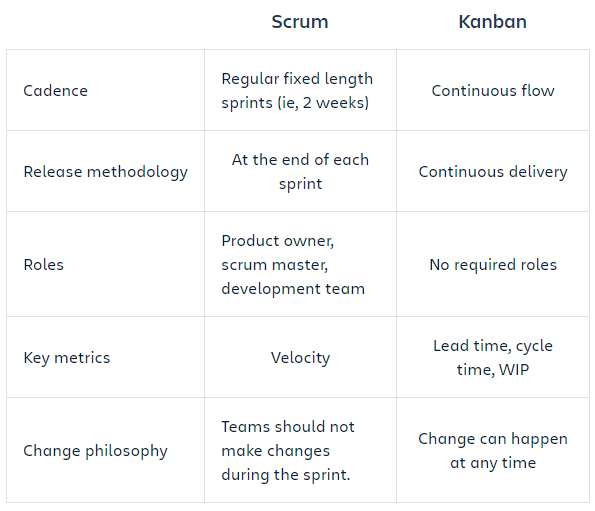
Hither's a tabular array illustrating the primary differences betwixt scrum and kanban. Source: Atlassian.com
Based on the above comparison, use scrum for characteristic-driven projects with regular release schedules, and use kanban for minor pieces of work such equally enhancements to an existing application.
It'due south likewise worth noting that many scrum teams use select aspects of kanban, specifically the kanban boards, for visual task management.
Scrum vs. extreme programming (XP)
XP is a software development approach that shares many similarities with scrum. Some of the major differences include:
- XP sprints last between 1-two weeks, while scrum sprints, on average, are 2-4 weeks long.
- Feature changes tin be fabricated in an XP iteration provided the feature hasn't been started yet. Scrum sprints don't let such changes.
- XP teams follow a strict club of priority usually determined past the client. In scrum project direction, the product owner determines which backlog items to prioritize, just the team can choose in which order to develop them depending on what makes the almost sense.
- XP prescribes software technology practices, such as exam-driven development and pair programming. Scrum doesn't.
Based on the in a higher place, choose scrum over XP if your sprints need to be longer than 1-2 weeks or XP over scrum if priority items need to be worked in order. XP is also more geared towards software evolution, while scrum is more versatile and tin can be used for other types of projects.
Choose the method and framework that fits your needs
Should you choose agile or scrum for project management?
The short respond: yes, definitely — if you need a methodology (active) and framework (scrum) that can go on upwardly with ofttimes changing client needs. Waterfall is not congenital for that level of adjustability.
The Motley Fool has a Disclosure Policy. The Author and/or The Motley Fool may have an interest in companies mentioned.
Source: https://www.fool.com/the-blueprint/agile-vs-scrum/
0 Response to "Everyting You Need to Know About Agile Crystal"
Post a Comment